Livestock farming is a vital pillar of Indian agriculture, contributing significantly to farm income, food security, employment, and rural livelihoods. With increasing demand for milk, meat, eggs, and value-added animal products, the livestock sector is undergoing rapid transformation through technology, improved breeding, and scientific management practices.
This blog explores the importance of livestock farming, emerging opportunities, key challenges, and future prospects, making it a comprehensive guide for farmers, students, and agripreneurs.
Importance of Livestock Farming
Livestock plays a multifunctional role in Indian agriculture. It supports crop farming, provides nutritional security, and acts as a safety net during crop failures.
Key Contributions:
- Contributes around 30% to agricultural GDP
- Source of regular income for small and marginal farmers
- Provides high-quality protein through milk, meat, and eggs
- Generates employment, especially for women and landless laborers
- Supports sustainable farming through manure and draft power
Livestock farming is especially important in rainfed and hilly regions where crop agriculture is risky.
Major Livestock Systems in India
1. Dairy Farming
India is the world’s largest milk producer. Dairy farming is dominated by smallholders owning 2–3 animals.
Key focus areas:
- Improved cattle and buffalo breeds
- Balanced feeding and fodder management
- Animal health and vaccination
- Milk value addition (curd, ghee, paneer)
2. Poultry Farming
Poultry is one of the fastest-growing livestock sectors.
Advantages:
- Low initial investment
- Quick returns
- High feed conversion efficiency
Broiler and layer farming provide income opportunities for rural youth and agristartups.
3. Goat and Sheep Farming
Often called the “poor man’s cow,” goat farming is highly suitable for:
- Dryland and hilly regions
- Small and marginal farmers
- Women and SHGs
Sheep and goats provide meat, milk, manure, and wool.
4. Pig Farming
Pig farming is gaining importance due to:
- High growth rate
- Efficient feed conversion
- Strong demand for pork in certain regions
It offers excellent scope for tribal and northeastern states.
Opportunities in Livestock Farming
1. Rising Demand for Animal Products
With population growth, urbanization, and rising incomes, demand for:
- Milk and dairy products
- Meat and eggs
- Processed animal products
is increasing rapidly, creating huge market opportunities.
2. Livestock-Based Entrepreneurship
Livestock farming supports diverse agribusiness ventures such as:
- Dairy processing units
- Feed and fodder production
- Breeding and artificial insemination services
- Organic manure and biogas units
This makes livestock a strong foundation for agripreneurship.
3. Integration with Crop Farming
Integrated farming systems (crop + livestock) improve:
- Resource recycling
- Soil fertility
- Farm sustainability
Livestock provides manure and income stability to crop farmers.
4. Government Support and Schemes
The Indian government promotes livestock development through schemes like:
- Rashtriya Gokul Mission
- National Livestock Mission
- Dairy Entrepreneurship Development Scheme
- Livestock Insurance Scheme
These initiatives support breed improvement, infrastructure, and farmer training.
Challenges in Livestock Farming
Despite its potential, livestock farming faces several challenges:
1. Feed and Fodder Shortage
India faces a significant deficit in:
- Green fodder
- Dry fodder
- Quality concentrate feed
This affects animal productivity and farmer profitability.
2. Animal Health and Disease Management
Diseases such as FMD, mastitis, and parasitic infections cause:
- Economic losses
- Reduced productivity
- Mortality
Limited access to veterinary services in rural areas worsens the problem.
3. Low Productivity
Indigenous breeds, though hardy, often have lower productivity due to:
- Poor nutrition
- Inadequate breeding practices
- Lack of scientific management
4. Climate Change Impact
Heat stress, water scarcity, and extreme weather events negatively impact:
- Milk yield
- Reproductive efficiency
- Animal health
Climate-resilient livestock practices are becoming essential.
Role of Technology in Livestock Farming
Modern livestock farming is increasingly technology-driven.
Key Innovations Include:
- Digital animal health records
- Sensor-based health and heat detection
- Mobile apps for ration balancing
- AI-based breeding and disease prediction
- Automated milking and feeding systems
These innovations improve productivity, reduce losses, and enhance decision-making.
Sustainable Livestock Farming Practices
Sustainability is crucial for the future of livestock farming.
Best Practices:
- Balanced and locally available feed resources
- Scientific waste management
- Biogas and manure recycling
- Ethical animal welfare practices
- Reduced antibiotic use
Sustainable livestock systems ensure long-term profitability and environmental safety.
Role of Livestock in Rural Development
Livestock farming empowers:
- Small farmers
- Women entrepreneurs
- Rural youth
It provides daily income, improves nutrition, and strengthens rural economies. Women play a major role in feeding, milking, and animal care, making livestock a key tool for gender-inclusive development.
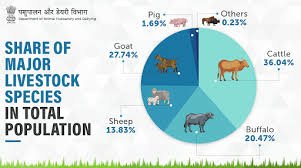
Future Prospects of Livestock Farming
The future of livestock farming in India is promising due to:
- Growing domestic demand
- Export potential of dairy and meat products
- Agritech innovations
- Focus on value addition and branding
- Policy support and investment
With scientific management and market integration, livestock farming can significantly contribute to doubling farmers’ income.
Conclusion
Livestock farming is not just a subsidiary activity—it is a powerful engine of agricultural growth and rural prosperity. By addressing challenges related to feed, health, and climate change and adopting modern technologies, livestock farming can become more productive, sustainable, and profitable.
A strong livestock sector is essential for building a resilient, inclusive, and nutrition-secure agricultural system in India.
Livestock farming, livestock farming in India, dairy farming, poultry farming, goat farming, livestock management, animal husbandry, sustainable livestock farming, livestock entrepreneurship
Gagan Tripathi is an agripreneur, plant scientist, and author known for his work in agritech innovation and sustainable horticulture. He is the Co-founder and CEO of Plant Orbit, a horticulture-focused startup dedicated to making healthy, scientifically managed plants accessible to urban and institutional consumers. Born in 2000, Gagan holds a master’s degree in Agriculture Extension and Communication, blending agricultural science with entrepreneurship and community outreach. He is also the author of the bestseller “Roadmap to Your Healthy Succulents”. His work focuses on sustainable plant care, green entrepreneurship, and building impact-driven agri startups in India.





Just swung by vipph77… pretty cool vibe, you guys. Games seem alright. Hopefully I can score big tonight!
Hey Everyone, Checking out vipph21!. It feels really cool. Seems promising. Aja!
Hey guys! Just checked out vipph1.org. Seems like a promising site. Anyone else tried it? Let me know what you think! vipph1